Background Color for Chart
(20 options)
White
Grey 95
Lemon Chiffon
Light Cyan
|
Color Palette for Bars
(4 options)
Bright Colors
Subdued Colors
Bright + Subdued
Black + White
|
First Color in Palette to Use
(10 options)
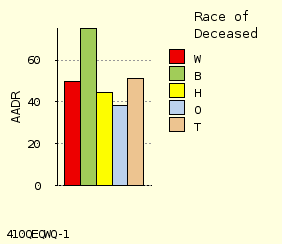
A Forward
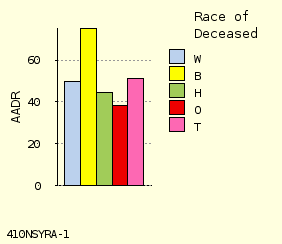
D Reverse
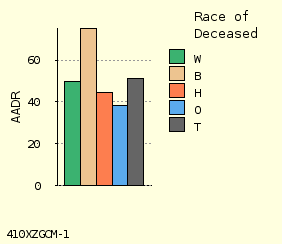
E Forward
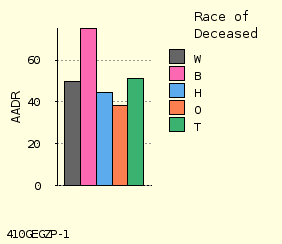
J Reverse
|
Vertical or Horizontal Bars
Vertical Bars
Horizontal
Stacked Bars?
Stacked Bars
Not Stacked
|
Height of Each Bar
(9 options)
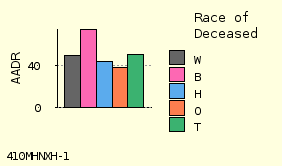
2 cm High
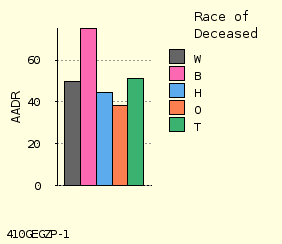
4 cm High
Width of Each Bar
(8 options)
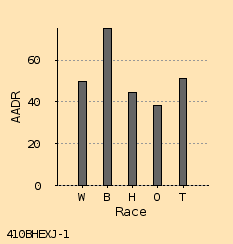
0.2 cm Wide
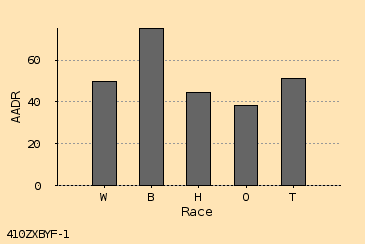
0.6 cm Wide
|
Include Grid Lines?
Include Grid
Omit Grid
Font Size for Chart Text
(8 options)
10 pt Font
14 pt Font
|
Background Color for Chart
(20 options)
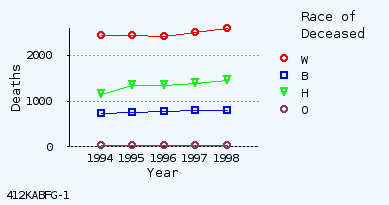
Alice Blue
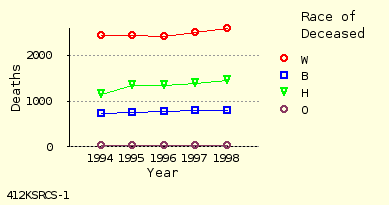
Light Yellow
|
Include Data Point Symbols?
(2 options)
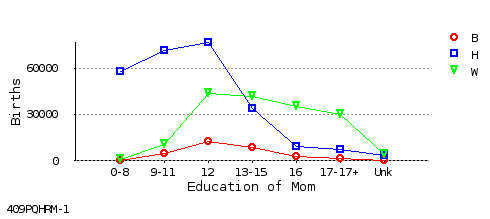
Include Symbols
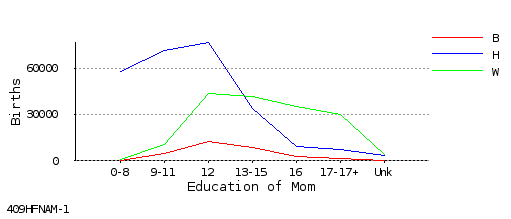
Omit Symbols
|
Radius for Chart Symbols
(10 options)
1.0 mm Radius
1.4 mm Radius
|
Line Chart Height
(9 options)
4.0 cm (Not Shown)
7.0 cm (Not Shown)
|
Width of Lines
(3 options)
Thin Lines
Thick Lines
|
Include Grid Lines?
(2 options)
Include Grid
Omit Grid
|
Colored Lines, or Black + White
(2 options)
Colored Lines
Black + White Lines
|
Font Size for Chart Text
(8 options)
10 pt Font (Not Shown)
12 pt Font (Not Shown)
|
Background Color for Chart
(20 options)
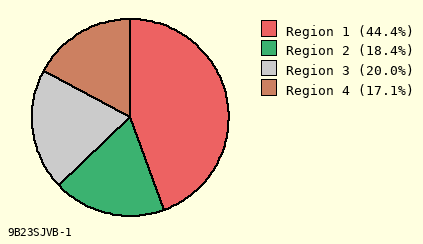
Cornsilk Background
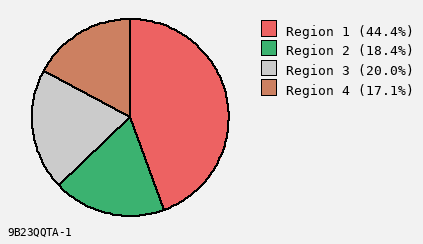
Grey Background
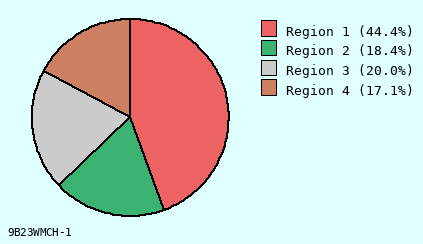
Light Cyan
|
Color Palette for Pie Chart
(3 options)
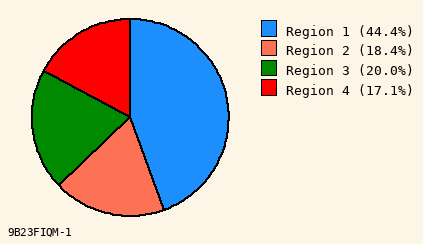
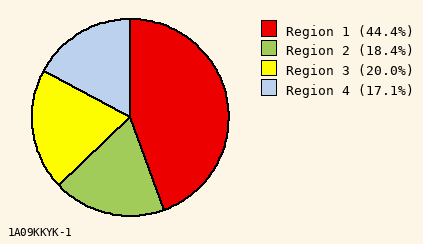
Bright Colors
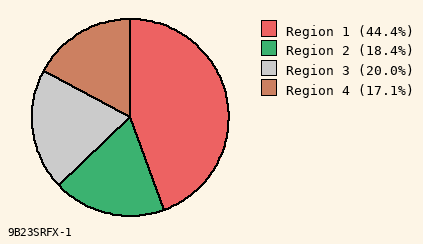
Subdued Colors
Mixed Colors
|
Slice #1 Color to Use
(10 options)
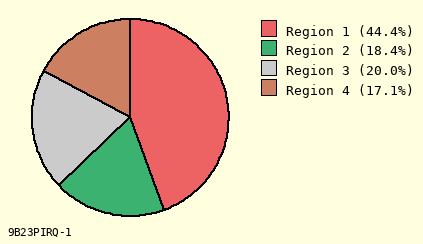
Color A for #1
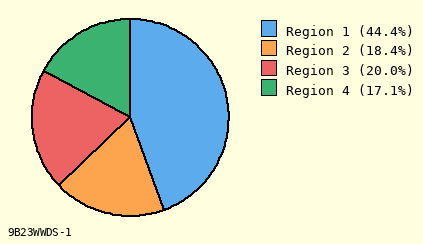
I Forward
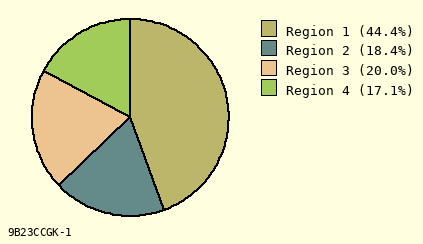
F Reverse
|
Slice #1 Clock Position
(12 options)
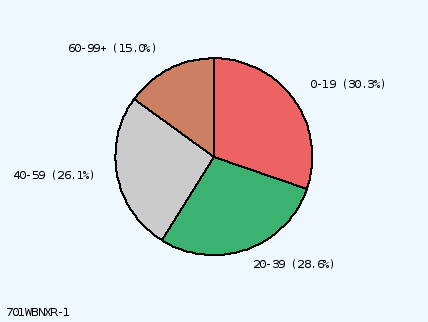
Slice #1 at Noon
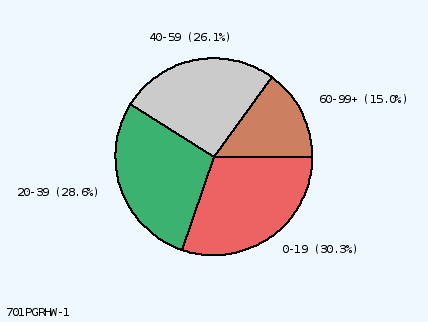
Slice #1 at 3:00
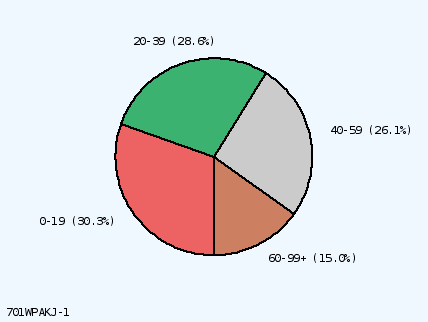
Slice #1 at 6:00
|
How to Label Pie Chart
(9 options)
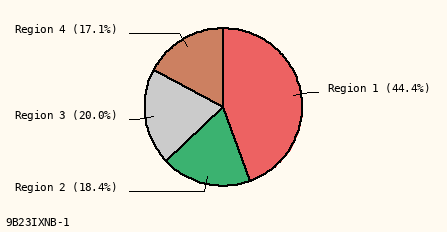
Line + Label
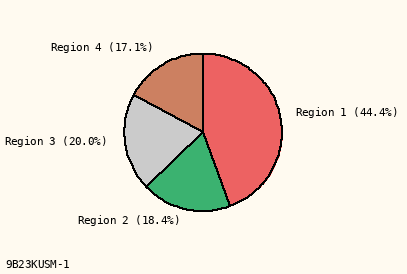
Label Only
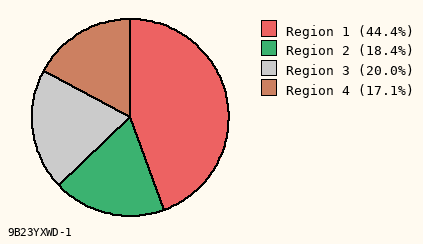
Use Legend
|
How to Display Slice Percents
(3 options)
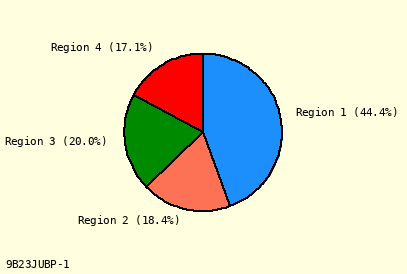
Percent After Label
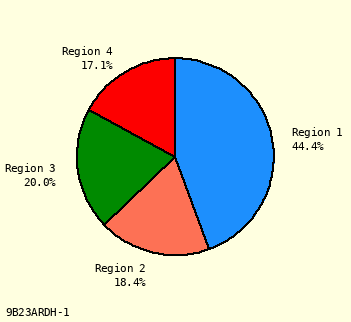
Under Label
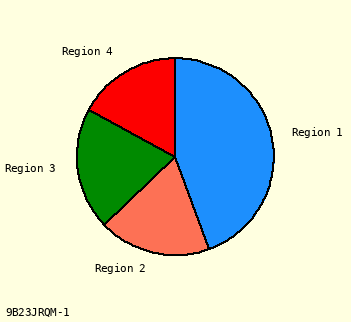
Omit Percents
|
Pie Chart Radius
(9 options)
3.0 cm (Not Shown)
4.0 cm (Not Shown)
5.0 cm (Not Shown)
|
Color Combination
(36 options)
|
Number of Colors
(8 options)
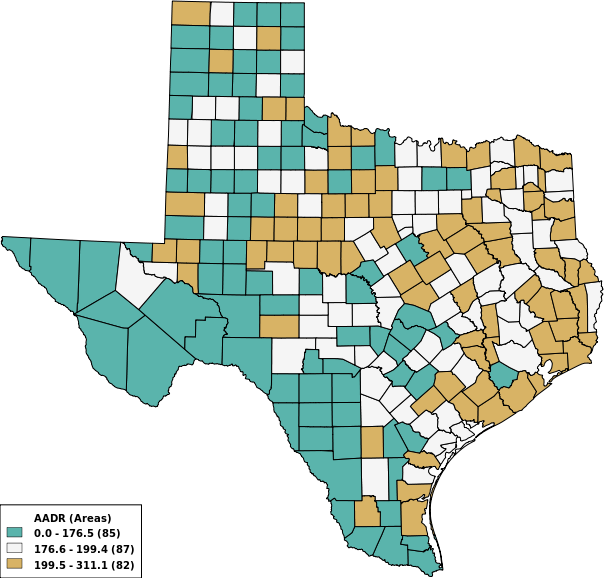
3 Colors
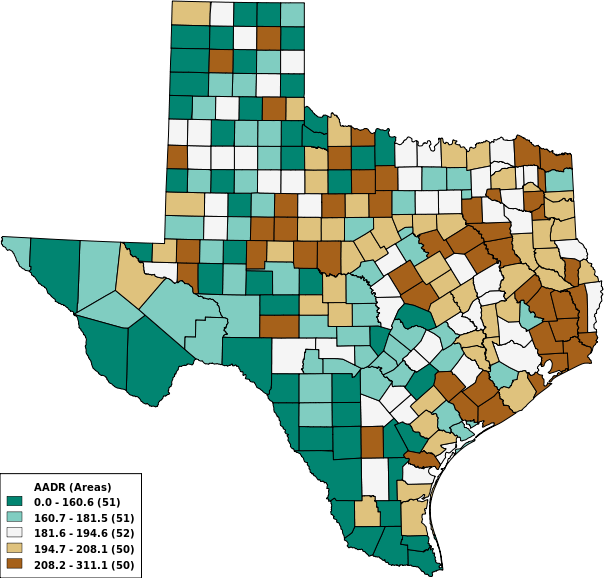
5 Colors
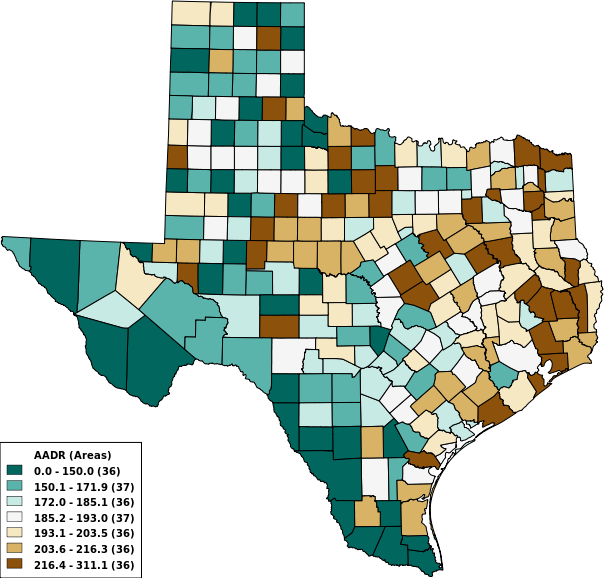
7 Colors
|
How to Set Ranges
(3 options)
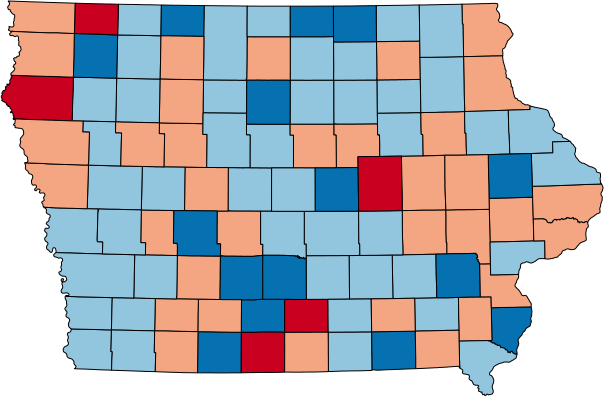
Equal Ranges
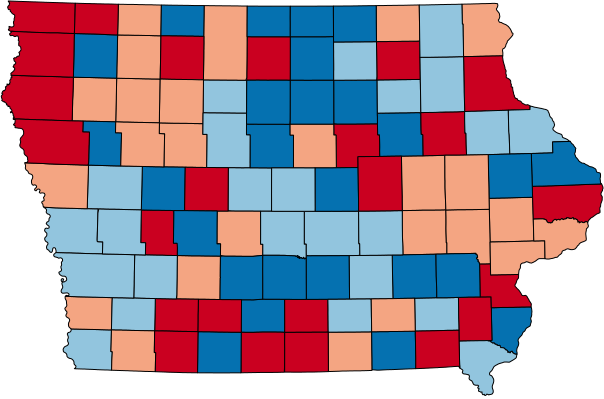
Equal Counts
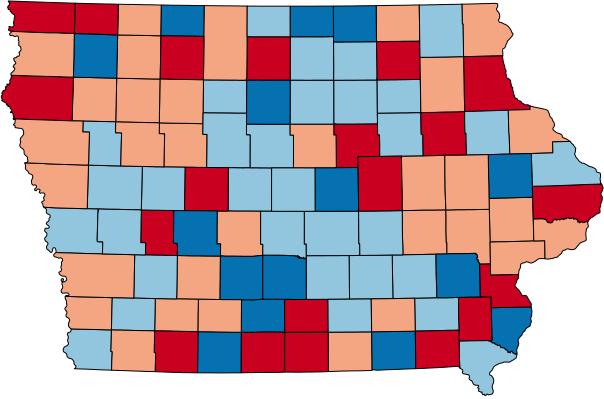
Natural Breaks
|
Boundaries to Display
(2 options)
County Boundaries
HSR Boundaries
Border Counties
|
Cell Suppression
(14 options)
Suppression Off
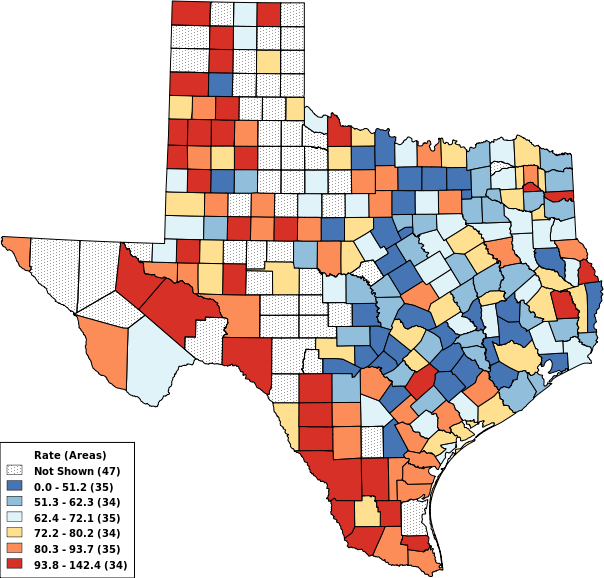
Suppress if < 10 Events
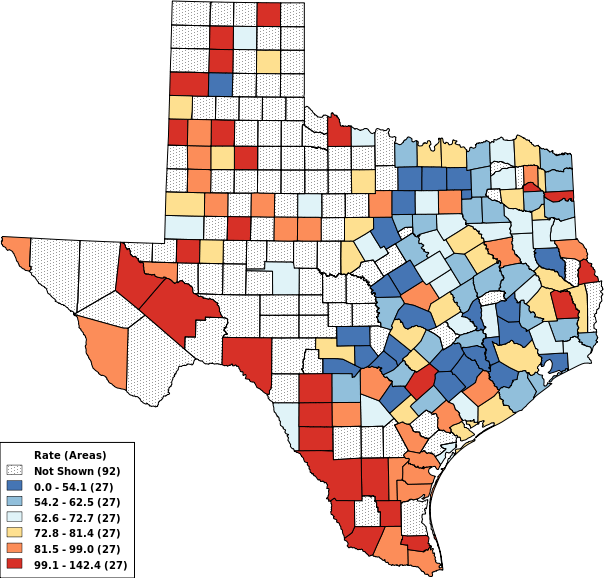
Suppress if < 30 Events
|
Map File Format
(PNG, PDF, SVG, GIS)
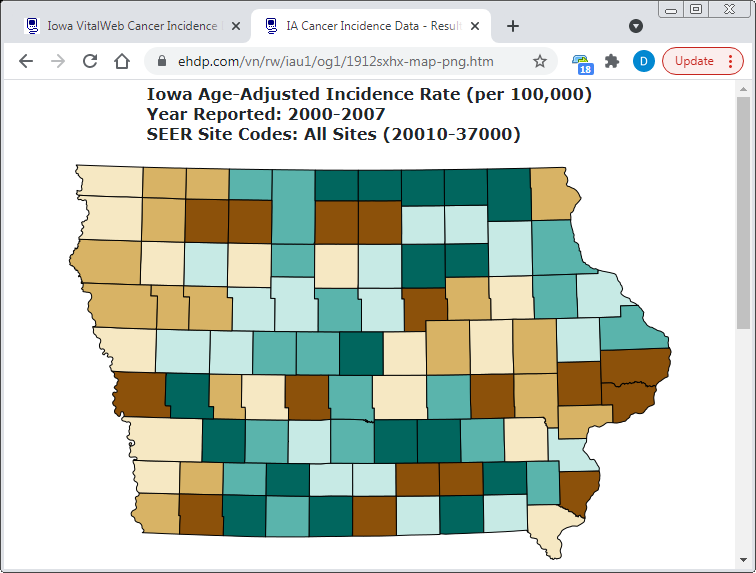
PNG Map (Imports Best)
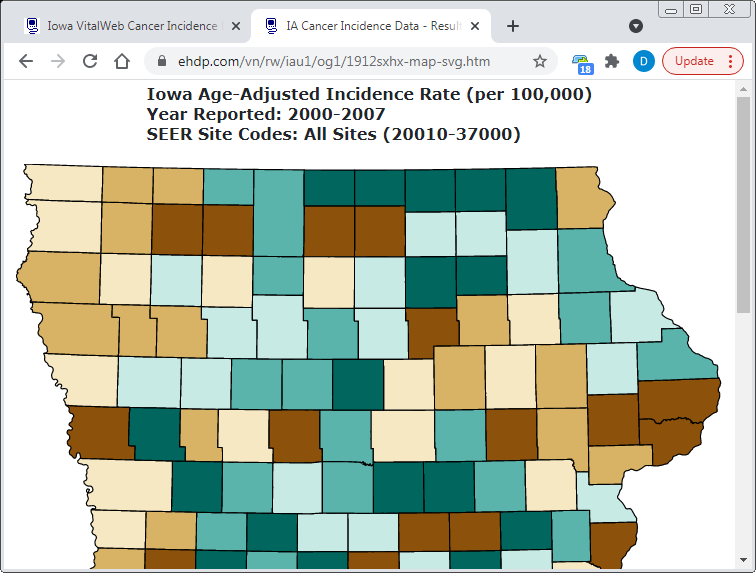
SVG Map (Prints Best)
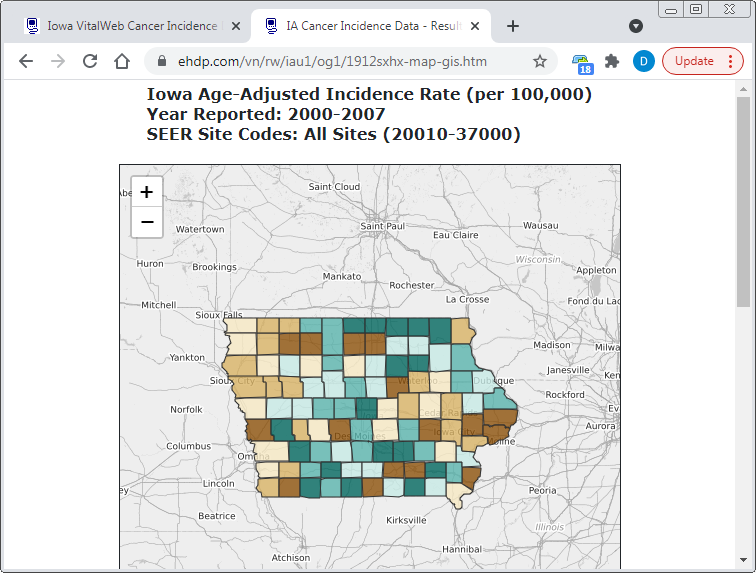
GIS Map (Interesting)
|